For those of us that work in the SEO/online marketing space, we have seen quite a bit of change in how SERPs have been presented to users over the years, and especially within the last few years. The way users are presented information is continuously evolving into a newly defined landscape where the process of actually sourcing/vetting/delivering the information you are obtaining is being truncated each and every day, wherever search engines see fit. Widely-used search engines like Google have been at the forefront of these innovations and the way their own SERP has evolved in the last two decades is nothing short of remarkable.
What is a SERP?
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page, which refers to the results feed that a user sees after searching for a query using a search engine, like Google or Bing.
What are SERPs Used For?
SERPs are primarily used to provide a user with a list of the most relevant results from the web in a response to a search query.
How Has Google’s SERP Evolved Over Time?
SERPs on the various search engines have evolved tremendously over the last 20 years, but especially within the last few years with the massive overhaul of introducing AI generated query answers, like AIOs. Here is a breakdown of the evolution of SERPs over time:
1998: Google Takes the Scene
Google actually began back in 1995 at Stanford, when founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who were both Ph.D. students, started working on a research project originally called BackRub. The name would later be changed to Google, which was a misspelled version of Googol, which is the number 1 followed by 100 zeros.

Google in December 1998
1999-2004: The Commercial Launch
This period marked tremendous evolution and development of Google’s SERP with the introduction of several major features, including:
- Google AdWords – Launched in 2000, this introduced the first paid search advertisements. They were text-only ads, which often appeared in the right-hand side of the page and sometimes at the very top.
- Google Image Search – Image results were launched in 2001, which added a new type of content that users could search for within Google. These images were not yet blended into the main SERP like they are today, but they did introduce the idea of vertical search.
- Algorithm Updates – Google began introducing algorithm updates for search in 2003. This was not a visual feature within the SERP, but it was a major shake up for the Google SERP due this update beginning to penalize spam and keyword stuffed pages.
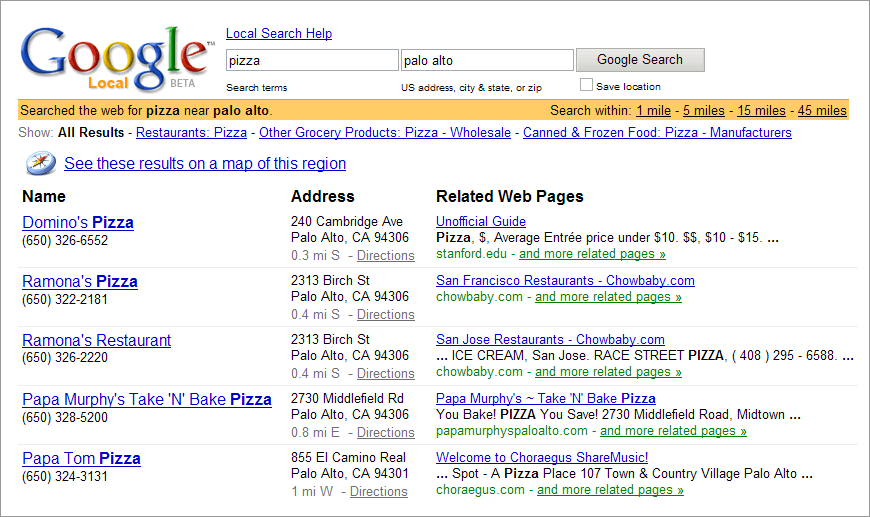
- Local Search – Local Search was rolled out in 2004, which was a major feature, introducing local business listings, maps, and directions for various queries with localized intent (coffee shop).
- Search Categories/Tabs – Categories like Google News and Google Scholar were officially launched within 2004 as well, which often appeared as tabs or options above the main results. This was a demonstration that this emerging tech company was growing beyond just general web pages.
Google Local Search Beta in 2004
2005-2010: The Universal Integration
Many refer to this period as the most revolutionary period of time for Google’s SERP, as it moved away from the “10 blue links” format and began delving into different types of media.
This massive development was primarily due to two major innovations, Universal Search and predictive/real-time features.
Early Enhancements & Personalized Results (2005-2006)
This period of time focused on refining the organic results in the Google SERP and introducing subtle, yet relevant user-specific elements:
- Sitelinks – Introduced in 2005, Sitelinks are nested links that appear indented beneath the main organic result for high-authority brands (Ex: searching Apple would display links below the URL in the SERP with Computers or Laptops linking to those interior pages). This was demonstrating Google’s trust in certain sites, which really was the early stages of Site Authority.
- Personalized Search – This also was rolled out in 2005, where Google started using user’s own search history to subtly and tastefully adjust the order of the organic results. If you were frequently visiting specific websites, that site would often be more likely to rank higher for you. This adjustment really was the catalyst of the SERP becoming unique to the user.
- Google Acquires YouTube – Google acquired YouTube in 2006. While this was not an instantaneous change in the SERP, this acquisition paved the way for the gigantic integration of video results (typically with thumbnails) that would soon arrive to the SERP.
Universal Search Revolution (2007)
The Universal Search developments were single largest visual and structural change during the period, where specialized search engines were merged into one unified SERP.
Universal Search ended the era of the separate search categories (Ex: only seeing 10 web links). Alternatively, the tech giant began blending the results from its vertical engines (local, video, news, images) directly into the main search results feed. For the very first time, a search query could return an image block, a video thumbnail, and a news story alongside the classic blue links.
Search Options Panel (2007)
During this time, Google also introduced the Search Options Panel, which was a panel that appeared on the left-hand side of the SERP, allowing users to be able to filter results by category (news, images, web). This feature allowed for users to gain more control over the newly blended results feed.
Real-Time and Predictive Search (2008-2010)
This period emphasized a major focus on shifting towards speed, prediction, and leveraging relevant/current information in the SERPs. Here are some milestone SERP updates that came during this time:
- Google Suggest – Launched in 2008. This feature introduced the predictive search dropdown that would populate when a user started to search a query, making the experience more seamless by cutting down time and guiding the user towards a popular and relevant search.
- Real-Time Search – Launched in 2009. Google began integrating results from live streams like Facebook and Twitter directly into the SERP for breaking news or trending topics.
- Google Places/Maps – Launched in 2010. This was a rebrand and facelift of the original Google Business Center. This update provided more comprehensive business information and made the local search results much more professional and data-rich for not only the benefit of the users, but also for the businesses as well.
- Caffeine Update – Launched in 2010. This was an algorithm update that despite not being visual, was a massive overhaul in how Google was indexing and crawling, which became much faster meaning that the information on the SERP was much more fresh and current.

Google Places/Maps shortly after its launch
2010-2015: The Foundations for an Answer Engine
This period of time for Google SERP was pivotal in the sense that it transformed from a list-based index to an answer engine. This evolution was comprised of large data initiatives, as well as major algorithm updates, with a core focus on quality and the experience on mobile devices.
The Shift to Semantic Search (2012-2014)
The most visible changes within this time period were Google’s move toward understanding the real meaning of entities instead of matching keywords. Several key developments that originated during this time frame:
- Knowledge Graph – Launched in 2012. The release of the knowledge graph was a monumental shift for Google. This feature displayed structured information about people, places, and things. The Knowledge Graph information is sourced from a vast database of verified information to answer queries quickly.
- Hummingbird Algorithm – Launched in 2013. This was a substantial algo update that fundamentally shifted the way Google processed queries. With this change, it allowed Google to better understand the context of long, more conversational queries, which also made things like the Knowledge Graph and other direct answers much more effective.
- Featured Snippets – Launched in 2014. Originally called Quick Answers, this feature allowed the Google to extract a direct and concise answer from an authoritative web page and display it in a large box above the organic results (also referred to as Position Zero). This was a pivotal moment in moving more towards a zero-click approach to search.
- HTTPS as a Ranking Signal – Rolled out in 2014. During this time Google began favoring websites that utilized HTTPS (secured connections), which led to the gradual appearance of the lock icons and “Secure” designations alongside URLs in the search, which displayed security and trust to users.
Quality & Mobile Takeover
During these years at Google, there were huge amounts of time and effort put into the development into cleaning up low-quality websites and preventing them from displaying in the SERP, as well as a major focus on optimizing the SERP and overall experience for mobile devices.
- Panda Algorithm Update – Rolled out in 2011. This update was done to combat “content farms” and low-quality, duplicate, or thin content from ranking in the SERPs.
- Penguin Algorithm Update – Rolled out in 2012. This update targeted web spam and overall manipulation, with a focus on cracking down on sites that used unnatural or “black hat” link techniques. This was yet another initiative to enhance the overall trust of the pages that did rank.
- Mobile-Friendly Update – Rolled out in 2015. This update benefited sites that had proper optimization and structure for mobile devices. This update was huge because it made it clear that revising your site to have mobile compatibility was not optional in order to rank well.
- RankBrain – Launched in 2015. Was introduced as part of the Hummingbird update, RankBrain utilized machine learning to better understand and interpret ambiguous or novel search queries that Google may have not seen before. This change made the SERP feel more intelligent and human-like.
It was very clear that by the end of 2015, the Google SERP was no longer just a tool for finding some links, but rather a curated and intelligent system designed to deliver facts directly to the user.
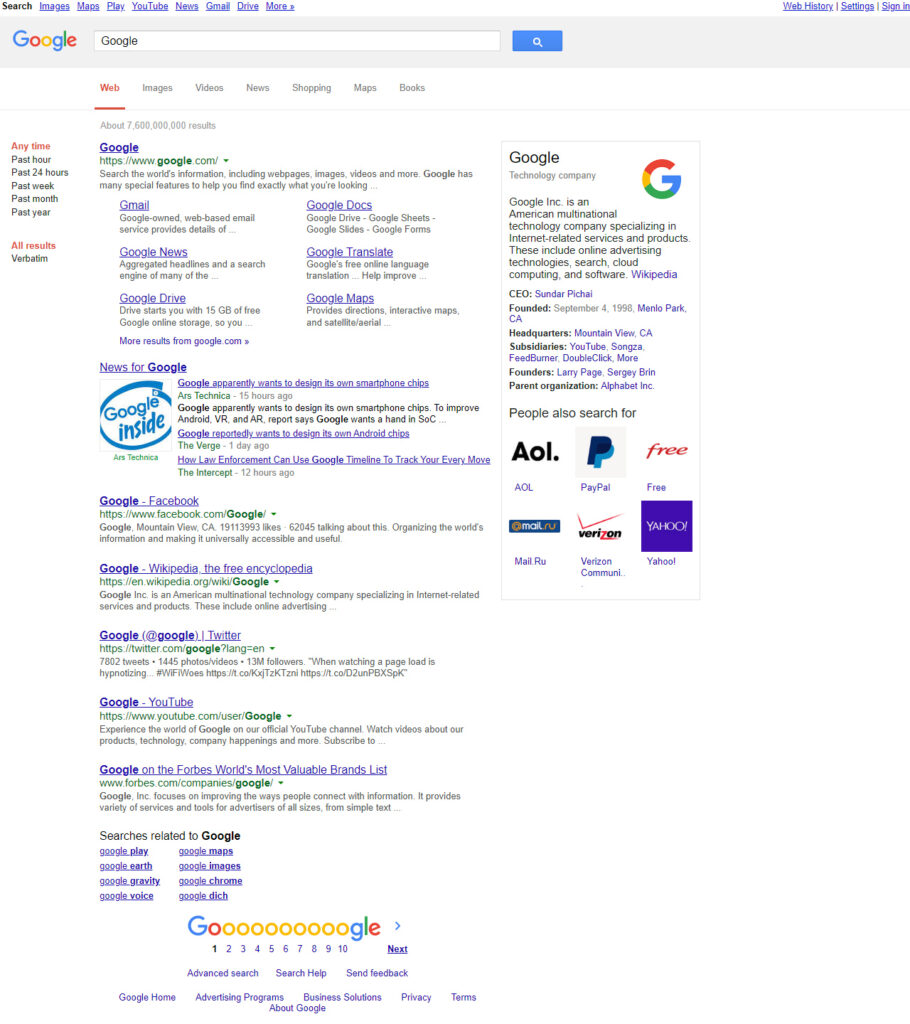
Google SERP in 2015
2015-2020: A Mobile & Intent-Focused SERP
From 2015 until 2020 marked Google’s SERP evolution into a highly interactive, mobile-centric, and overall intent-focused interface. Google began its journey into AI advancements during this time, with a goal of providing comprehensive answers to users directly on the SERP, which further reduce the need for users to click links.
The Rise of the Zero-Click (2015-2017)
During this time period, Google perfected its direct-answer features, which made the SERP a much more conversational and overall dynamic experience. Some updates made during this time:
- People Also Asked (PAA) – Launched in 2015. This featured displayed a box of a nested, dynamic list of questions that were directly related to the user’s initial query. This update encouraged users to explorer other related searches without needing to search for a new query. This also led to increased time within the SERP.
- Mobile-First Indexing Shift – Started rolling out in 2015. During this period, Google gradually began to shift its primary index to use the mobile version of a website for ranking and indexing. This change forced all SERP designs and contents of websites to prioritize the mobile experience.
- New Ad Label Design – Launched in 2017. The existing yellow, boxed “Ad” label for paid results was replaced with a cleaner and smaller black bolded “Ad” text on a white background. This change made it so the paid results blended in more within the SERP.
- Refinements to Featured Snippets – Rolled out in 2017. Google adjusted the featured snippets so that they began appearing in more complex formats, including tables, video suggestions, and multiple images. This change led to an increase in prevalence across a wider variety of query types.
AI Developments and Visual Richness (2018-2020)
Towards the end of the decade, there was a major focus on deep machine learning to understand language and the ability to leverage structured data for highly visual results. Some updates made during this period:
- Job Postings Feature – Launched in 2018. Google launched a dedicated Job Postings or Google for Jobs feature, which displayed a rich, structured block of job listings at the top of the SERP for relevant queries, often sourcing data directly from job boards.
- BERT Algorithm Update – Rolled out in 2019. BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. This allowed for Googler to understand the context and nuances of conversational and complex queries much better than it could before. This was really beneficial for long-tail search queries.
- Favicons in Organic Results (Mobile) – Launched in 2019. Google started to display favicons (small website icons) next to the organic result for sites on mobile (and briefly on desktop). This was a cool new way to brand a website and increase overall visual separation from site to site.
- Review Snippets/Rich Results Expansion – Rolled out in 2019. With proper use of the necessary structured data (schema markup), sites were now able to have review snippets populate directly under sites in the SERP, which could include star ratings, price, product availability).
- Focus on Core Web Vitals – Initiated in 2020. While the official page experience update was made slightly later, Google began to emphasize their site speed tool/metric called Core Web Vitals, which focused on site speed, interactivity, and visual stability, as a ranking factor. This pressured websites to improve their user experience to enhance not only UX, but also their rankings.
By the end of this decade, the Google SERP was largely being defined by its interactivity, visual complexity, and reliance on AI to serve answers directly to users. This typically pushed the classic “10 blue links” well below the top of the fold.

Example of a Review Snippet populating in the SERP
2020-2025: Generative AI Has Entered the Building
Many will say that this time period has reflected the most aggressive and rapid evolution of the Google SERP since its inception. This era can be defined by the full integration/adoption of generative AI and a heavy emphasis on content quality.
The Push for Quality & Trust (2020-2022)
This initial phase of this time period for the Google SERP saw a focus on improving the trustworthiness and real-world value of the content that was displaying within the SERPs, especially after the Covid-19 pandemic. Some changes we saw during this period:
- Core Web Vitals Ranking Signal – Initiated in 2021. Google officially announces that Core Web Vitals would be a ranking factor for organic results.
- Product Reviews Updates – Rolled out in 2021. During this time, Google made a series of updates that rewarded content written by SMEs (subject matter experts) who demonstrated actual hands-on experience with the product mentioned and not just summaries.
- Helpful Content System – Launched in 2022. Google announced the Helpful Content Update, which was designed to elevate content created with the intent of serving people, rather than search engines. Basically, in a simple way, Google started to rank content that was written for the actual intent it served and not just to rank well higher in the SERP. This update heavily penalized sites with content that was perceived as lower quality, duplicated, or written with software.
- EAT –> EEAT – Launched in 2022. Google’s quality guidelines were officially updated to include a focus on Experience. This shift put a heavy pressure on who was creating the content that would appear in the SERPs.
The Revolution of Generative AI (2023-Current)
It is easy to say that this time period was the defining development of this five year span. Google began to fundamentally change the SERP structure and challenged its own 25 year old model of search. Some of the major changes during this period:
- Search Engine Experience (SGE) Beta – Launched in 2023. Google announced and launched the experimental phase of SGE, which would later come to be known as the infamous AI Overviews. This new feature utilized generative AI to synthesize information from multiple sources and create a conversational and comprehensive summary at the VERY TOP OF THE SERP.
- AIO Official Launch – Launched in 2024. AI Overviews officially rolled out during this time, initially within the US and then rapidly expended out globally. AIOs completely changed the structure of the SERP in two major ways:
- Provided an answer without the user needing to click anywhere (increasing the overall zero-click based searches)
- Citing sources from the SERP, but often showing priority to articles that were not displaying in the top organic positions.
- Revamped Mobile/Desktop Visual Design – Launched in 2024. Paired with the freshly launched AIOs, Google shifted the desktop SERP with the AIO on the left and the panel of source citations populating on the right for easier cross-referencing.
- AI Mode/Complex Query Capabilities – Rolled out in 2025. Google began to test and roll out a more dedicated AI Mode or AI Chat within the actual SERP, which allowed users to ask complex and multi-faceted questions. From this, Google would spin out long and conversational multi-step reasoning from the AI, which further merged the search box with an AI chatbot.
- Discussions/Forums Feature – Launched in 2025. The Google SERP started to increasingly incorporate a dedicated Discussions and Forums block, often featuring results from Reddit and other community-based platforms, which recognized that user-generated experience is a valuable signal for a plethora of search queries.
The 2020-2025 era of the Google SERP finalized its transition into an AI-first platform. The focus of the SERP shifted to delivering the answers directly within the SERP, rather than just providing links to the answer. The introduction of AI Overviews has largely been considered the most impactful development the tech giant has made since the Knowledge Graph in 2012.
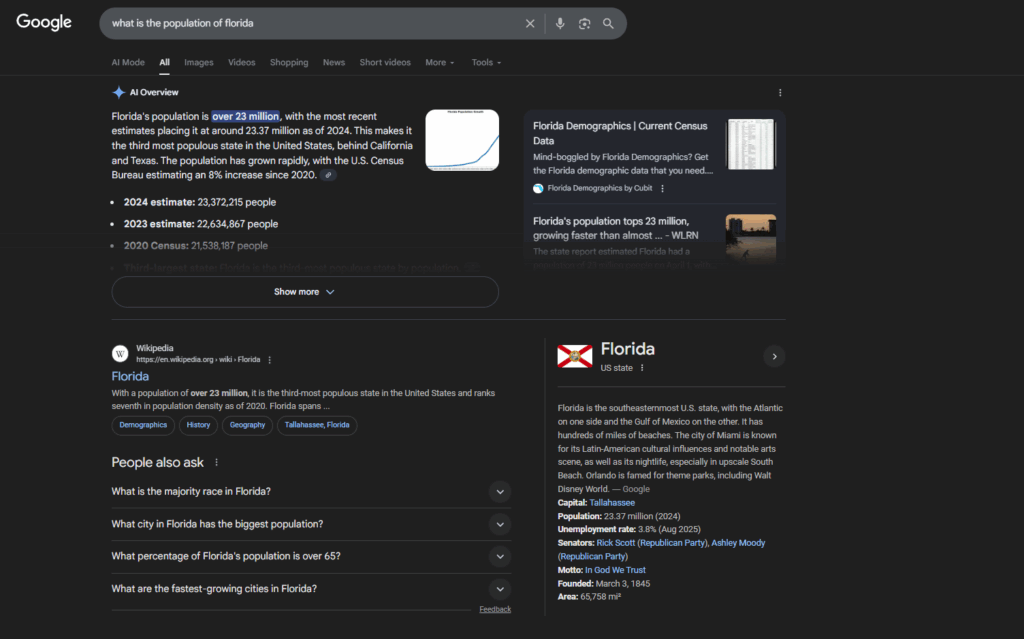
What the Google SERP looks like for me when testing a search query